Researchers on the Tokyo Institute of Expertise have made important developments in reminiscence know-how utilizing multiferroic supplies, particularly BFCO nanodots. These supplies allow extra energy-efficient information writing utilizing electrical fields and non-destructive studying by magnetic fields. Credit score: SciTechDaily.com
Tokyo Institute of Expertise researchers have developed BFCO nanodots for environment friendly and non-destructive reminiscence know-how, promising developments in low-power magnetic reminiscence units.
Conventional reminiscence units are risky and the present non-volatile ones depend on both ferromagnetic or ferroelectric supplies for information storage. In ferromagnetic units, information is written or saved by aligning magnetic moments, whereas in ferroelectric units, information storage depends on the alignment of electrical dipoles. Nevertheless, producing and manipulating magnetic fields is energy-intensive, and in ferroelectric reminiscence units, studying information destroys the polarized state, requiring the reminiscence cell to be re-writing.
Developments in Multiferroic Supplies
Multiferroic supplies, which include each ferroelectric and ferromagnetic orders, supply a promising resolution for extra environment friendly and versatile reminiscence know-how. Cobalt-substituted BiFeO3 (BiFe0.9Co0.1O3, BFCO) is a multiferroic materials that displays sturdy magnetoelectric coupling, which means modifications in electrical polarization have an effect on magnetization. Consequently, information may be written utilizing electrical fields, which is extra energy-efficient than producing magnetic fields, and skim utilizing magnetic fields, which avoids the damaging read-out course of.
In a major milestone for multiferroic reminiscence units, a crew of researchers led by Professor Masaki Azuma and Assistant Professor Kei Shigematsu from Tokyo Institute of Expertise in Japan has efficiently developed nanodots with single ferroelectric and ferromagnetic domains.
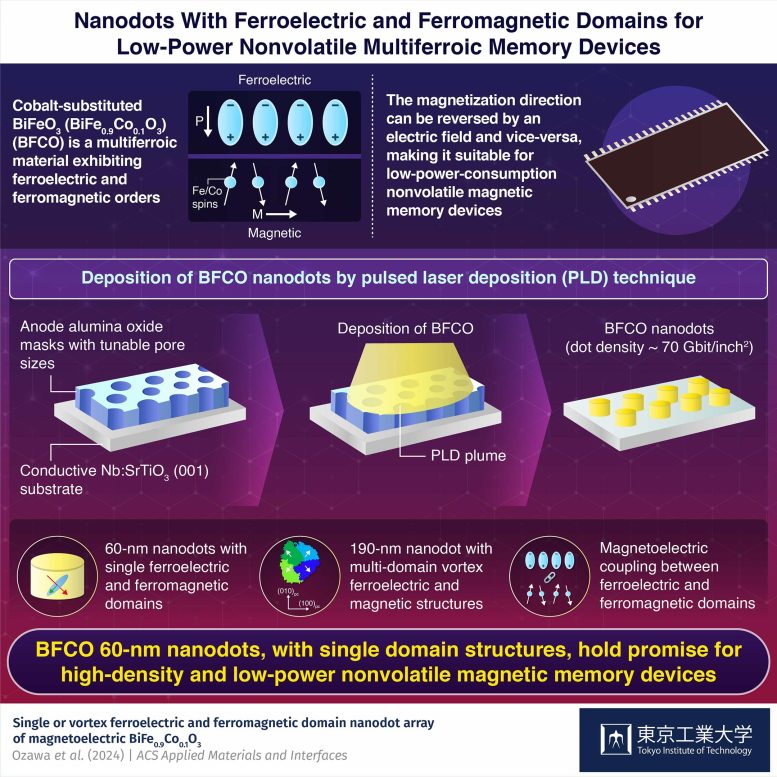
BFCO 60-nm nanodots, with single area buildings, maintain promise for high-density and low-power nonvolatile magnetic reminiscence units. Credit score: Tokyo Tech
Collaborative Analysis Efforts
“At “Sumitomo Chemical Subsequent-Technology Eco-Pleasant Units Collaborative Analysis Cluster” inside the Institute for Revolutionary Analysis at Tokyo Institute of Expertise, there’s a deal with multiferroic supplies that exhibit cross-correlation responses between magnetic and electrical properties primarily based on the rules of strongly correlated electron programs. The middle goals to develop supplies and processes for next-generation low-power non-volatile magnetic reminiscence units, in addition to to conduct reliability assessments and social implementation,” says Azuma.
Methodology and Findings
Of their examine printed within the journal ACS Utilized Supplies and Interfaces on April 9, 2024, researchers utilized pulsed laser deposition to deposit multiferroic BFCO onto a conductive Nb:SrTiO3 (001) substrate. They managed the deposition course of through the use of anodized aluminum oxide (AAO) masks with adjustable pore sizes, leading to nanodots with diameters of 60 nm and 190 nm.
BFCO is a promising possibility for low-power, nonvolatile magnetic reminiscence units as its magnetization route may be reversed with an electrical subject. On observing the polarization and magnetization instructions utilizing piezoresponse pressure microscopy and magnetic pressure microscopy, respectively, the researchers discovered that the nanodots exhibit correlated ferroelectric and ferromagnetic area buildings.
Observations on Area Buildings
Apparently, when evaluating nanodots of various sizes, they seen important variations. The smaller 60-nm nanodot, made utilizing an oxalic acid AAO masks, confirmed single ferroelectric and ferromagnetic domains, the place the polarization and magnetization instructions are uniform all through. Nevertheless, the bigger 190-nm nanodot, fashioned utilizing a malonic acid AAO masks, had multi-domain vortex ferroelectric and magnetic buildings indicating sturdy magnetoelectric coupling.
“Such a single-domain construction of ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism could be a super platform for investigating BFCO as an electric-field writing magnetic read-out reminiscence system, and multi-domain buildings supply a playground for elementary analysis,” remarks Shigematsu.
Nonvolatile magnetic reminiscence units are essential for numerous digital purposes as they preserve saved info even when energy is turned off. With their distinctive composition of single ferromagnetic and ferroelectric domains, BFCO 60-nm nanodots present nice potential for creating magnetic reminiscence units that require minimal electrical energy for writing and studying operations.
Reference: “Single or Vortex Ferroelectric and Ferromagnetic Area Nanodot Array of Magnetoelectric BiFe0.9Co0.1O3” by Keita Ozawa, Yasuhito Nagase, Marin Katsumata, Kei Shigematsu and Masaki Azuma, 9 April 2024, ACS Utilized Supplies & Interfaces.
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c01232