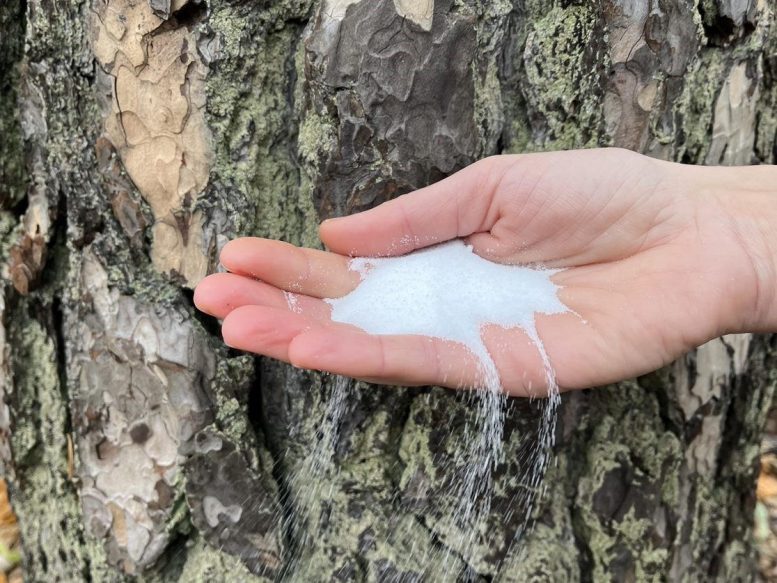
Sodium-ion batteries comprise sodium – a quite common substance present in desk salt – as an alternative of lithium. Credit score: Chalmers
As society shifts away from fossil fuels, the demand for batteries is surging. Concurrently, this surge is prone to result in a shortage of lithium and cobalt, important components in prevalent battery varieties. An alternate resolution might be sodium-ion batteries, which primarily make the most of desk salt and biomass derived from the forestry sector as their uncooked supplies.
Now, researchers from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, present that these sodium-ion batteries have an equal local weather affect as their lithium-ion counterparts – with out the chance of working out of uncooked supplies.
“The supplies we use within the batteries of the long run will probably be essential so as to have the ability to swap to renewable power and a fossil-free automobile fleet,” says Rickard Arvidsson, Affiliate Professor of Environmental Methods Evaluation at Chalmers.
Based on the European Fee’s Essential Uncooked Supplies Act, the demand for important uncooked battery supplies is predicted to extend exponentially as EU international locations transition to renewable power methods and electrical automobiles. The inexperienced transition may even require extra native manufacturing of batteries and different new fossil-free applied sciences, and a gradual provide of uncooked supplies is required to fulfill demand. On the identical time, such manufacturing carries a excessive danger of provide disruptions, because of the restricted variety of sources for uncooked supplies.
“Lithium-ion batteries have gotten a dominant know-how on the earth and they’re higher for the local weather than fossil-based know-how is, particularly with regards to transport. However lithium poses a bottleneck. You may’t produce lithium-based batteries on the identical charge as you wish to produce electrical vehicles, and the deposits danger being depleted in the long run,” says Rickard Arvidsson. Along with this, important battery supplies, equivalent to lithium and cobalt, are largely mined in only a few locations on the earth, posing a danger to the availability.
Sodium-ion batteries supply promising know-how
The event of recent battery applied sciences is transferring quick within the quest for the following technology of sustainable power storage – which ought to ideally have an extended lifetime, have a excessive power density, and be straightforward to supply. The analysis workforce at Chalmers selected to take a look at sodium-ion batteries, which comprise sodium – a quite common substance present in frequent sodium chloride – as an alternative of lithium. In a brand new examine, they’ve carried out a so-called life cycle evaluation of the batteries, the place they’ve examined their complete environmental and useful resource affect throughout uncooked materials extraction and manufacturing.

Rickard Arvidsson, Affiliate Professor, Division of Know-how Economics and Administration, Chalmers College of Know-how, Sweden. Credit score: Chalmers
“We got here to the conclusion that sodium-ion batteries are significantly better than lithium-ion batteries when it comes to affect on mineral useful resource shortage, and equal when it comes to local weather affect. Relying on which situation you take a look at, they find yourself at between 60 and simply over 100 kilograms of carbon dioxide equivalents per kilowatt hour theoretical electrical energy storage capability, which is decrease than beforehand reported for any such sodium-ion battery. It’s clearly a promising know-how,” says Rickard Arvidsson.
The researchers additionally recognized various measures with the potential to additional cut back local weather affect, equivalent to growing an environmentally higher electrolyte, because it accounted for a big a part of the battery’s complete affect.
Inexperienced power requires power storage
At this time’s sodium-ion batteries are already anticipated for use for stationary power storage within the electrical energy grid, and with continued improvement, they’ll in all probability even be utilized in electrical automobiles sooner or later.
“Power storage is a prerequisite for the enlargement of wind and solar energy. Provided that the storage is finished predominantly with batteries, the query is what these batteries will probably be constituted of? Elevated demand for lithium and cobalt might be an impediment to this improvement,” says Rickard Arvidsson.
The foremost benefit of the know-how is that the supplies within the sodium-ion batteries are considerable and will be discovered everywhere in the world. One electrode within the batteries – the cathode – has sodium ions as a cost service, and the opposite electrode – the anode – consists of onerous carbon, which in one of many examples the Chalmers researchers have investigated will be produced from biomass from the forest business. When it comes to manufacturing processes and geopolitics, sodium-ion batteries are additionally an alternate that may speed up the transition to a fossil-free society.
“Batteries primarily based on considerable uncooked supplies might cut back geopolitical dangers and dependencies on particular areas, each for battery producers and international locations,” says Rickard Arvidsson.
Extra in regards to the examine
The examine is a potential life cycle evaluation of two totally different sodium-ion battery cells the place the environmental and useful resource affect is calculated from cradle to gate, i.e. from uncooked materials extraction to the manufacture of a battery cell. The purposeful unit of the examine is 1 kWh theoretical electrical energy storage capability on the cell degree.
Each varieties of battery cells are primarily primarily based on considerable uncooked supplies. The anode is made up of onerous carbon from both bio-based lignin or fossil uncooked supplies, and the cathode is made up of so-called “Prussian white” (consisting of sodium, iron, carbon, and nitrogen). The electrolyte incorporates a sodium salt. The manufacturing is modeled to correspond to a future, large-scale manufacturing. For instance, the precise manufacturing of the battery cell relies on at the moment’s large-scale manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries in gigafactories.
Two totally different electrical energy mixes had been examined, in addition to two several types of so-called allocation strategies – that’s, allocation of sources and emissions. One the place the local weather and useful resource affect is distributed between coproducts primarily based on mass, and one methodology the place all affect is allotted to the principle product (the sodium-ion battery and its parts and supplies).
Reference: “Potential life cycle evaluation of sodium-ion batteries constituted of considerable components” by Sanna Wickerts, Rickard Arvidsson, Anders Nordelöf, Magdalena Svanström and Patrik Johansson, 13 November 2023, Journal of Industrial Ecology.
DOI: 10.1111/jiec.13452
The examine was funded by the Swedish Power Company via the Battery Fund Program.