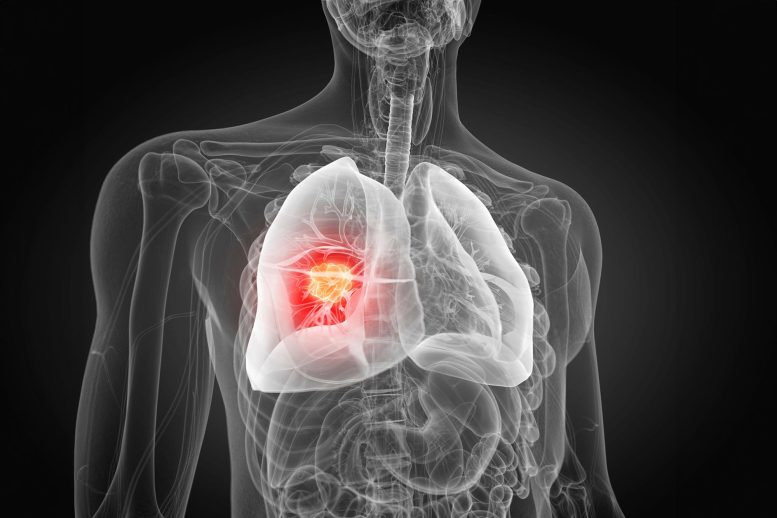
Analysis reveals that non-smokers with non-small cell lung most cancers (NSCLC) usually resist focused remedies on account of mutations within the EGFR and p53 genes, which result in genome doubling and drug resistance. This has important implications for therapy methods and diagnostic assessments.
Researchers have found the rationale why focused therapy for non-small cell lung most cancers fails to work for some sufferers, significantly those that have by no means smoked.
The examine reveals that lung most cancers cells with two specific genetic mutations usually tend to double their genome, which helps them to resist therapy and develop resistance to it. Performed by researchers from UCL, the Francis Crick Institute, and AstraZeneca, the examine is printed immediately (June 13) within the journal Nature Communications.
Epidemiology and Genetic Components of NSCLC
Within the UK, lung most cancers is the third commonest kind of most cancers and the main reason behind most cancers demise. Round 85% of sufferers with lung most cancers have non-small cell lung most cancers (NSCLC), and that is the most typical kind present in sufferers who’ve by no means smoked. Thought-about individually, ‘by no means smoked’ lung most cancers is the fifth commonest reason behind most cancers demise on this planet.
The most typical genetic mutation present in NSCLC is within the epidermal progress issue receptor gene (EGFR), which permits most cancers cells to develop sooner. It’s present in about 10-15% of NSCLC circumstances within the UK, significantly in sufferers who’ve by no means smoked.
Challenges of Present Remedies
Survival charges range relying on how superior the most cancers is, with solely round a 3rd of sufferers with Stage IV NSCLC and an EGFR mutation surviving for as much as three years.
Lung most cancers remedies that concentrate on this mutation, referred to as EGFR inhibitors, have been accessible for over 15 years. Nonetheless, whereas some sufferers see their most cancers tumors shrink with EGFR inhibitors, different sufferers, significantly these with a further mutation within the p53 gene (which performs a job in tumor suppression), fail to reply and expertise far worse survival charges. However scientists and clinicians have to date been unable to elucidate why that is the case.
Insights From New Analysis
To seek out the reply, the researchers re-analyzed information from trials of the latest EGFR inhibitor, Osimertinib, developed by AstraZeneca. They checked out baseline scans and first follow-up scans taken a number of months into therapy for sufferers with both EGFR-only or with EGFR and p53 mutations.
The crew in contrast each tumor on the scans, excess of had been measured within the authentic trial. They discovered that for sufferers with simply the EGFR mutations, all tumors received smaller in response to therapy. However for sufferers with each mutations, whereas some tumors had shrunk others had grown, offering proof of speedy drug resistance. This sample of response, when some however not all areas of a most cancers are shrinking in response to a drug therapy inside a person affected person, is named a ‘combined response’ and is a problem for oncologists caring for sufferers with most cancers.
Research Findings and Future Implications
To research why some tumors in these sufferers could be extra susceptible to drug resistance, the crew then studied a mouse mannequin with each the EGFR and p53 mutation. They discovered that inside resistant tumors in these mice, way more most cancers cells had doubled their genome, giving them further copies of all their chromosomes.
The researchers then handled lung most cancers cells within the lab, some with simply the only EGFR mutation and a few with each mutations, with an EGFR inhibitor. They discovered that inside 5 weeks of publicity to the drug, a considerably greater proportion of cells with each the double mutation and double genomes had multiplied into new drug-resistant cells.
Towards Higher Diagnostic Instruments
Professor Charles Swanton, from UCL Most cancers Institute and the Francis Crick Institute, mentioned: “We’ve proven why having a p53 mutation is related to worse survival in sufferers with non-smoking associated lung most cancers, which is the mix of EGFR and p53 mutations enabling genome doubling. This will increase the danger of drug-resistant cells growing by chromosomal instability.”
Non-small cell lung most cancers sufferers are already examined for EGFR and p53 mutations, however there’s at the moment no normal check to detect the presence of entire genome doubling. The researchers are already seeking to develop a diagnostic check for medical use.
Scientific Purposes and Future Analysis
Dr. Crispin Hiley, from UCL Most cancers Institute and a Guide Scientific Oncologist at UCLH, mentioned: “As soon as we will establish sufferers with each EGFR and p53 mutations whose tumours show entire genome doubling, we will then deal with these sufferers in a extra selective method. This would possibly imply extra intensive comply with up, early radiotherapy or ablation to focus on resistant tumors, or early use of combos of EGFR inhibitors, similar to Osimertinib, with different medicine together with chemotherapy.”
Reference: “Heterogeneous responses to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition in non-small cell lung most cancers end result from chromosomal instability facilitated by entire genome doubling and TP53 co-mutation” by Sebastijan Hobor, Maise Al Bakir, Crispin T. Hiley and Marcin Skrzypski et al., 13 June 2024, Nature Communications.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-47606-9
This work was supported by the Francis Crick Institute, which receives its core funding from Most cancers Analysis UK, the UK Medical Analysis Council, and Wellcome.