A human can’t survive within the Mariana Trench with out safety. At its deepest, the ditch plunges 35,000 ft beneath the floor of the Pacific Ocean to a area reigned by crushing strain and darkness.
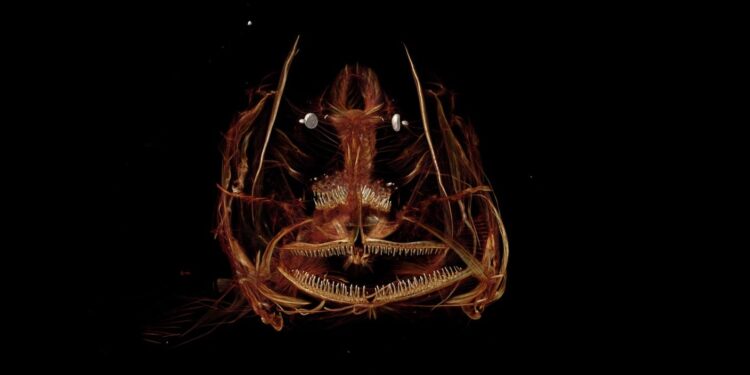
But someway life finds a means. The hadal snailfish, with delicate fins and translucent physique, roams the darkish and freezing waters. Big shrimp-like creatures as much as a foot lengthy scavenge fallen particles, together with wood and plastic, and transparent eels with fish-like heads hunt prey. A carpet of micro organism breaks down useless sea creatures and plankton to recycle vitamins.
We’ve solely scratched the floor of what thrives within the deepest areas of the ocean. However a big mission has now added over 6,000 new microbes to the deep-sea species tally.
Referred to as the Mariana Trench Environment and Ecology Research Project, or MEER for brief, a group of scientists have collected sediment from the hadal zone—the deepest a part of the ocean—within the Mariana Trench and two different areas. The investigation revealed hundreds of recent species and two diversifications permitting the microbes to thrive below intense strain.
Another team assembled the genomes of 11 deep-sea fish and located a mutated gene that would increase their capability to outlive. Sequencing the genome of an enormous shrimp-like creature recommended micro organism boosted its metabolism to adapt to high-pressure environments.
Learning these mysterious species might yield new medications to combat infections, irritation, and even most cancers. They present how creatures adapt to excessive environments, which could possibly be helpful for engineering pressure- or radiation-resistant proteins for space exploration.
“The deep sea, particularly hadal zones, represents among the most excessive and least explored environments on Earth,” wrote examine creator Shunping He and colleagues on the Chinese language Academy of Sciences. The mission hopes to “push the boundaries of our understanding of life” on this alien world, added Shanshan Liu and her group at BGI research, in a separate examine.
Meet MEER
Oceans cowl roughly 70 % of the Earth’s floor. But we all know little or no about their inhabitants, particularly on the ocean ground.
Because the Nineteen Sixties, a number of missions—some autonomous, others manned—have sought to discover the deepest a part of the Pacific Ocean, the Mariana Trench. Over 30,000 ft deep, it might fully submerge Mount Everest.
The ditch is an unforgiving atmosphere. The strain is over 1,000 occasions higher than that at sea stage, and at Challenger Deep—the deepest level navigated up to now—the temperature is simply above freezing. The seabed there’s shrouded in full darkness.
But a manned descent 65 years in the past discovered flatfish and enormous shrimp-like creatures thriving within the trench—the primary indicators that life might survive in such excessive environments. Extra not too long ago, James Cameron, greatest recognized for guiding movies like Titanic, dived to almost 36,000 ft and took footage that helped identify even more new species.
The deep sea, it appears, is a trove of alien species but to be found. The MEER mission is gathering specimens from the deepest trenches internationally to study extra.
MEER depends on a deep-sea submersible referred to as Fendouzhe, which suggests striver or fighter in Chinese language. Fendouzhe is self-propelled and might survive freezing temperatures and large strain. It holds three crew members and has two mechanical arms bristling with units—cameras, sonars, drills.
The submersible reached the underside of the Mariana Trench in 2020 adopted by missions to the Yap Trench and Philippine Basin. Scientists on board gathered over 1,600 sediment samples from a number of hadal zones between 6 and 11 kilometers, or roughly 4 to 7 miles, below the ocean.
Added to the punishing strain and lack of sunshine, the deep sea is low on environmental vitamins. It’s actually “a singular mixture that units it aside from all different marine and terrestrial environments,” wrote the authors.
Undersea Genes
Sediments maintain genetic materials that survives intact when delivered to the floor for evaluation.
One examine sketched a panorama of dwelling creatures within the deep ocean utilizing an method referred to as metagenomics. Right here, scientists sequenced genetic materials from all microbes inside an atmosphere, permitting them to reconstruct a birds-eye view of the ecology.
On this case, the gathering is “10-fold bigger than all beforehand reported,” wrote the group. Over 89 % of the genomes are totally new, suggesting most belong to beforehand unknown microbial species dwelling within the deep ocean.
Samples collected from different trenches have various genetic profiles, suggesting the microbes realized to adapt to numerous deep ocean environments. However they share related genetic modifications. A number of genes bump up their capability to digest toluene as meals. The chemical is usually recognized for manufacturing paints, plastics, drugs, and cosmetics.
Different genes wipe out metabolic waste merchandise referred to as reactive oxygen species. In giant quantities, these injury DNA and result in growing older and illness. The creatures even have a beefed-up DNA restore system. This might assist them adapt to intense strain and frigid temperatures, each of which enhance the probabilities of these damaging chemical compounds wreaking havoc.
Deep-Sea Superpowers
In the meantime, different research peered into the genetic make-up of fish and shrimp-like creatures within the hadal zone.
In a single, scientists collected samples utilizing the Fendouzhe submersible and an autonomous rover, masking areas from the Mariana Trench to the Indian Ocean. The group zeroed in on roughly 230 genes in deep-sea fish that increase survival below strain.
Most of those assist restore DNA injury. Others enhance muscle operate. Surprisingly, all 11 species of deep-sea fish studied shared a single genetic mutation. Engineering the identical mutation in lab-grown cells helped them extra effectively flip DNA directions into RNA—step one cells take when making the proteins that coordinate our bodily capabilities.
That is “more likely to be advantageous within the deep-sea atmosphere,” wrote the group.
Prime predators within the deep depend on a gradual provide of prey—primarily, a shrimp-like species referred to as amphipods. Entire genome sequencing of those creatures confirmed the shrimp thrive thanks to numerous good micro organism that assist them defend in opposition to different bacterial species.
There are additionally another intriguing findings. For instance, whereas most deep-sea fish have misplaced genes related to imaginative and prescient, one species confirmed gene exercise associated to paint imaginative and prescient. These genes are just like ours and will doubtlessly allow them to see colour even in complete darkness.
Scientists are nonetheless digging via the MEER database. The coalition hopes to bolster our understanding of probably the most resilient lifeforms on Earth—and doubtlessly encourage journeys into different excessive environments, like outer area.