Grabbing a espresso cup appears simple. However you want to have the ability to transfer your hand, stretch it out, and maintain it regular.
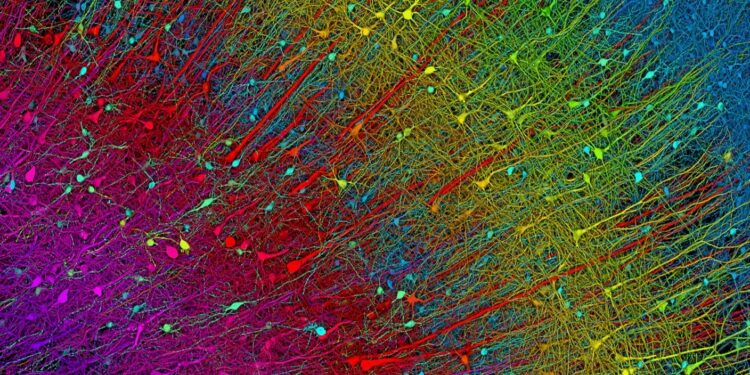
These actions are tough for folks with Parkinson’s illness. The dysfunction eats away at mind cells—known as dopamine neurons—that management motion and emotion. Signs start with tremors. Then muscular tissues lock up. Finally, the illness makes strolling and sleeping tough. Considering will get more durable, and as neurons die, folks lose their focus and reminiscence.
Medicines can maintain some signs at bay, however finally, their results put on off. For almost half a century, scientists have been exploring another resolution: Changing dying dopamine neurons with new ones.
This month, two studies of almost two dozen folks with Parkinson’s confirmed the technique is protected. A single transplant boosted dopamine ranges for 18 months with out notable unintended effects. Sufferers had fewer motor signs even after they stopped taking their common medicines.
The work stands out as a result of as a substitute of being tailor-made to every affected person, the cells have been ready-made. The groups grew new dopamine neurons from donors within the lab. These cells can multiply simply in petri dishes, forming a big provide of alternative cells for sufferers.
Malin Parmar at Lund College, who was not concerned within the research, told Nature the outcomes are “a giant leap within the discipline.”
A Deteriorating Mind
Parkinson’s is the world’s second most typical neurodegenerative illness, with as much as 90,000 new instances a yr within the US. Michael J. Fox, who performed Marty McFly in Again to the Future and launched a foundation to discover a Parkinson’s remedy, is probably probably the most well-known particular person residing with the illness.
In Parkinson’s, neurons in the midst of the mind steadily die. Known as the substantia nigra, the area is intricately linked with surrounding areas and is crucial for motion and feelings. Though the whole space finally deteriorates, neurons that pump out dopamine—a chemical that fine-tunes neural networks and features—are first to go. This implies the mind steadily loses dopamine because the illness progresses.
There are therapies however no cures.
One frequent medicine, Levodopa, tackles signs. Neurons slurp up the drug and rework it into dopamine. However as mind cells steadily die, the medicine turns into much less efficient. Levodopa additionally has unintended effects. As a result of midbrain wiring influences each addictive behaviors and motor management, flooding it with dopamine can change how folks act, like growing the risk of gambling addiction and different obsessive behaviors. Lengthy-term use may set off random actions of the face, arms, and legs—a symptom known as dyskinesia.
Mind implants that bridge damaged connections within the midbrain are one other remedy. Deep mind stimulation, for instance, mimics natural brain signals to ease motor signs. Some implants are already approved to be used, however they require surgical procedure and monitoring and aren’t extensively accessible.
Moderately than patching a damaged circuit with a short lived repair, what if we may substitute damaged dopamine neurons with recent ones?
Stem-Cell Marathon
Stem cells supply an answer. These particular cells can develop into some other kind of cell underneath the correct situations, making them the proper alternative for dying neurons.
Again within the Eighties, one staff transplanted mind tissue wealthy in dopamine neurons into folks with Parkinson’s. These sufferers skilled a boost of dopamine and improved motor management for years after the surgical procedure. However the supply was extremely controversial: fetal mind tissue.
Though a “first proof-of-concept for cell transplantation remedy,” the trial raised “moral issues,” according to Hideyuki Okano on the Keio College Regenerative Medication Analysis Heart in Japan, who was not concerned within the new research.
In its place, scientists have realized to create stem cells within the lab. One methodology produces stem cell traces that may develop nearly eternally underneath the correct situations. In one other, scientists chemically rework grownup cells, usually taken from the pores and skin, right into a stem-cell-like state. These are known as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). 5 years in the past, a team transformed iPSCs into dopamine neurons and transplanted them right into a affected person, bettering signs for as much as two years.
Getting sufficient of the cells is tough. Fetal brains are laborious to return by and ethically problematic. And making iPSCs for every affected person is time-consuming, doubtlessly limiting widespread adoption.
Off-the-Shelf Remedy
The brand new research took a unique strategy: They gathered two kinds of extensively out there stem cells, turned them into younger dopamine neurons, and implanted them into the mind.
In one trial, researchers injected cells from a human embryonic-stem-cell line into the midbrains of 12 middle-aged folks with Parkinson’s. As soon as a line is established, these lab-grown cells can reproduce indefinitely, primarily making them a vast useful resource.
Individuals acquired almost three million cells unfold throughout 18 areas within the midbrain. Some 300,000 of those—roughly the variety of dopamine cells that naturally inhabit the area—survived transplantation. The sufferers took immunosuppressant medication for a yr to stop rejection.
Observe-up mind scans discovered greater ranges of dopamine, even after sufferers stopped medicine 18 months later. Nobody confirmed indicators of most cancers—a critical danger related to stem-cell remedy—wrote Okano. Signs improved 50 p.c. Ache went down. And sufferers reported improved sleep, urge for food, and each day motion.
In a second study, scientists created an iPSC cell line from a donor’s pores and skin cells and coaxed them into recent dopamine neurons. Transplanted into seven Parkinson’s sufferers, the cells have been proven to be protected and in working order. They pumped out dopamine and eased motor signs for over two years.
These research stand out as a result of they used donor cells, versus cells tailor-made to every affected person. “The outcomes are encouraging as a result of they present that using allogeneic (non-self) transplants for the remedy of Parkinson’s illness is more likely to be protected,” wrote Okano.
Lengthy Highway Forward
Although promising, each research have limitations, particularly the big variety of cells concerned. It’s attainable to develop the cells in a standard lab setting, however high quality management and different particular measures are essential. Scientists are nonetheless debating if off-the-shelf cell therapies—which require immunosuppressants—are higher than personalised therapies.
The brand new strategy additionally must bear bigger trials. Each research have been open label, that means contributors knew they have been being handled, doubtlessly triggering placebo results. Nonetheless, the therapies are shifting ahead. Each groups are working with biotechnology companies to check them in bigger teams.
“Transplanting dopamine-releasing neurons into the mind is a promising regenerative remedy for Parkinson’s illness,” wrote Okano. However “extra proof is required to show its effectiveness.”