Spirals of photo voltaic wind can spin off bigger photo voltaic eruptions and disrupt Earth’s magnetic area, but they’re too tough to detect with our present single-location warning system, based on a brand new examine.
However a constellation of spacecraft, together with one which sails on daylight, may assist discover the tornado-like options in time to guard gear on Earth and in orbit.
The examine outcomes come from pc simulations of an enormous cloud of plasma erupting from the solar and transferring via the photo voltaic system. As a result of the simulation covers options that span distances 3 times Earth’s diameter right down to 1000’s of miles, the researchers may decide how smaller, tornado-like spirals of plasma and magnetic area—known as flux ropes—change into regarding options in their very own proper.
“Our simulation exhibits that the magnetic area in these vortices will be sturdy sufficient to set off a geomagnetic storm and trigger some actual hassle,” says Chip Manchester, analysis professor of local weather and area sciences and engineering and the corresponding writer of the within the Astrophysical Journal.
In Might 2024, a geomagnetic storm tripped high-voltage energy strains, disrupted satellite tv for pc orbits, and compelled some airplanes to vary course. It additionally scrambled navigation programs on tractors within the Midwest, which NASA says value every affected farm $17,000 in damages, on common. For each scientific curiosity and higher warning programs forward of those occasions, NASA and the Nationwide Science Basis funded this examine.
Geomagnetic storms are triggered by magnetic fields within the solar wind, a bubble of plasma that flows outward from the solar and envelops the photo voltaic system. Like wind on Earth, the photo voltaic wind blows in various patterns that comprise area climate. Eruptions on the solar create probably the most excessive area climate—dense, fast-moving clouds of plasma known as coronal mass ejections that span 34 million miles, on common.
However scientists have additionally seen comparatively small flux ropes within the photo voltaic wind, between 3,000 and 6 million miles vast. These options are too small for typical simulations of coronal mass ejections, which may solely produce options bigger than 7 million miles vast, however they’re additionally too massive for simulations typically used to check magnetic fields and plasma particles within the photo voltaic wind. The brand new simulation permits researchers to see these options of intermediate dimension together with massive coronal mass ejections.
The brand new simulation urged that the tornado-like flux ropes type out of the coronal mass ejections as they drive via slower photo voltaic wind, flinging apart spinning plenty of plasma like a snowplow tossing snow. Some tornadoes dissipate, however extra persistent vortices can type throughout collisions with neighboring streams of quick and sluggish photo voltaic wind. Telescopes pointing on the solar search for eruptions to warn of dangerous area climate, however for flux ropes, the researchers say that’s not sufficient.
“If there are hazards forming out in area between the solar and Earth, we will’t simply have a look at the solar,” says examine coauthor Mojtaba Akhavan-Tafti, affiliate analysis scientist of local weather and area sciences and engineering.
“This can be a matter of nationwide safety. We have to proactively discover buildings like these Earth-bound flux ropes and predict what they’ll appear to be at Earth to make dependable area climate warnings for electrical grid planners, airline dispatchers and farmers.”
The photo voltaic wind can solely set off geomagnetic storms when its magnetic area has a powerful southward orientation. Spacecraft stationed between Earth and the solar already assist scientists make area climate warnings by measuring the pace of the photo voltaic wind, in addition to the power and route of its magnetic area. However a photo voltaic eruption aimed away from Earth, or with northward-pointing magnetic fields, may nonetheless toss vortices with southward-pointing magnetic fields towards Earth. These tornadoes would go unnoticed in the event that they miss the probes stationed at L1.
“Think about for those who may solely monitor a hurricane remotely with the measurements from one wind gauge,” Manchester says. “You’d see a change within the measurements, however you wouldn’t see the storm’s total construction. That’s the present state of affairs with single-spacecraft programs. We’d like viewpoints from a number of area climate stations.”
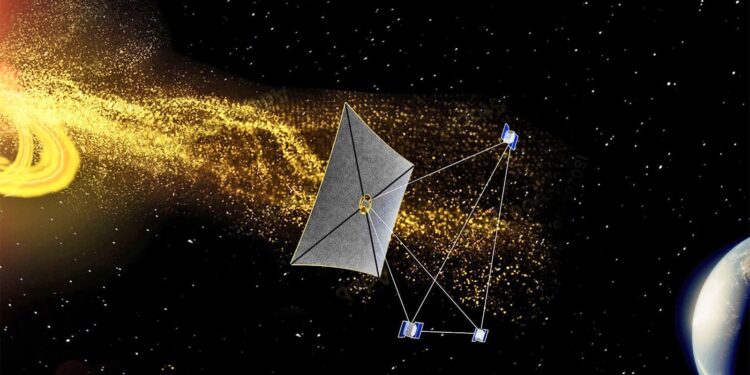
The researchers hope to offer that multiprobe view of photo voltaic tornadoes with a constellation of spacecraft known as the Area Climate Investigation Frontier, or SWIFT, which was developed in a NASA mission idea examine led by Akhavan-Tafti.
Within the present proposal, 4 probes can be stationed in a triangular-pyramid formation, round 200,000 miles aside. Three equivalent probes would occupy every nook of the pyramid’s base, situated in a airplane round L1. A last “hub spacecraft,” situated past L1, would function the pyramid’s apex, pointing towards the solar. This configuration would enable SWIFT to see how the photo voltaic wind adjustments on its strategy to Earth, and its hub nearer to the solar may make area climate warnings 40% quicker.
The apex’s location would usually require an impractical quantity of gasoline to struggle the solar’s gravity, however NASA engineers, via their Photo voltaic Cruiser mission, designed an aluminum sail that would allow the probe to park past L1. The sail would cowl a couple of third of a soccer area, permitting it to catch sufficient photons to keep up the spacecraft’s place with out burning gasoline.
Supply: University of Michigan