Gene modifying is a numbers recreation. For any genetic tweaks to have notable impression, a adequate variety of focused cells must have the disease-causing gene deleted or changed.
Regardless of a rising gene-editing arsenal, the instruments share a typical shortcoming: They solely work as soon as in no matter cells they attain. Viruses, in distinction, readily self-replicate by hijacking their host’s mobile equipment after which, their numbers swelling, drift to contaminate extra cells.
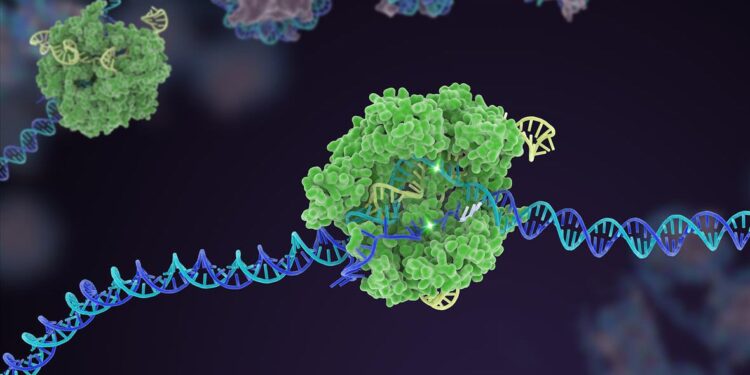
This technique impressed a workforce on the College of California, Berkeley and collaborators to change the gene editor, CRISPR-Cas9, to equally replicate and unfold to surrounding cells.
Led by gene-editing pioneer and Nobel Prize winner, Jennifer Doudna, the scientists added genetic directions for cells to make a virus-like transporter that may encapsulate the CRISPR equipment. As soon as manufactured in handled cells, the CRISPR cargo ships to neighboring cells.
The upgraded editor was roughly 3 times more practical at gene modifying lab-grown cells in comparison with commonplace CRISPR. It additionally lowered the quantity of a dangerous protein in mice with a genetic metabolic dysfunction, whereas the unique model had little impact on the similar dose.
The expertise is “a conceptual shift within the supply of therapeutic cargo,” wrote the workforce in a bioRxiv preprint.
Recoding Genetics
CRISPR has fully remodeled gene therapy. In only a few years, the expertise exploded from a analysis curiosity right into a biotechnology toolbox that may deal with beforehand untreatable inherited illnesses. Some CRISPR variations delete or inactivate pathogenic genes. Others swap out single mutated DNA letters to revive well being.
The primary CRISPR therapies concentrate on blood issues and require docs to take away cells from the physique for therapy. The therapies are tailor-made to every affected person however are sluggish and dear. To carry gene remedy to the plenty, scientists are growing gene editors that edit DNA straight contained in the physique with a single injection.
From reprogramming faulty blood cells and treating multiple blood disorders to lowering dangerous levels of cholesterol and tackling mitochondrial diseases, CRISPR has already confirmed it has the potential to unleash a brand new universe of gene therapies at breakneck speed.
Gene editors “promise to revolutionize medication by overriding or correcting the underlying genetic foundation of illness,” wrote the workforce. However all these instruments are throttled by one fundamental requirement: Sufficient cells need to be edited that they override their diseased counterparts.
What number of depends upon the genetic dysfunction. Therapies must appropriate round 20 percent of blood stem cells to maintain sickle cell illness at bay. For Duchenne muscular dystrophy, an inherited illness that weakens muscle tissue, over 15 percent of focused cells must be edited.
These numbers could seem low, however they’re nonetheless difficult for present CRISPR applied sciences.
“As soon as delivered to cells, modifying equipment is confined to the cells it initially enters,” wrote the workforce. To compensate, scientists typically enhance the dosage, however this dangers triggering immune assaults and off-target genetic edits.
Work Smarter, Not Tougher
Though membrane-bound and seemingly remoted, cells are literally fairly chatty.
Some cells package deal mRNA molecules into bubbles and eject them in direction of their neighbors, primarily sharing directions for learn how to make proteins. Different cells, including neurons, kind intensive nanotube networks that shuttle parts between cells, akin to energy-producing mitochondria.
Impressed by these mechanisms, scientists have transferred small proteins and RNA throughout cells. So, the workforce thought, why couldn’t the same mechanism unfold CRISPR too?
The workforce tailored a service developed a few years back from virus proteins. The proteins mechanically kind a hole shell that buds off from cells, drifts throughout to neighboring cells, and fuses with them to launch encapsulated cargo.
The system, known as NANoparticle-Induced Switch of Enzyme, or NANITE, combines genetic directions for the service molecules and CRISPR equipment right into a single round piece of DNA. This ensures the Cas9 enzyme is bodily linked to the supply proteins as each are being made inside a cell. It additionally means the ultimate supply automobile encapsulates information RNA as nicely, the “bloodhound” that tethers Cas9 to its DNA goal.
Like a benevolent virus, NANITE initially “infects” a small variety of cells. As soon as inside, it instructs every cell to make the total CRISPR software, package deal it up, and ship it alongside to different cells. Uninfected cells take in the cargo and are dosed with the gene editor, permitting it to unfold past handled cells.
In comparison with traditional CRISPR-Cas9, NANITE was roughly 3 times extra environment friendly at modifying a number of forms of cells grown in tradition. Including protein “hooks” helped NANITE find and latch on to particular populations of cells with an identical “eye” protein, rising modifying specificity. NANITE punched far past its weight: Edited cells averaged practically 300 p.c of the initially handled quantity, suggesting the remedy had unfold to untreated neighbors.
In one other take a look at, the workforce tailor-made NANITE to slash a disease-causing protein known as transthyretin within the livers of mice. Mutations to the protein ultimately result in coronary heart and nerve failure and might be lethal. The researchers injected NANITE straight into the rodents’ veins utilizing a high-pressure system. This method reliably sends round DNA to the liver, the goal organ for the illness, and shows promise in people.
Inside every week, NANITE had decreased transthyretin practically 50 p.c whereas modifying solely round 11 p.c of liver cells. Such outcomes would possible enhance and stabilize the illness in keeping with previous clinical trials, though the workforce didn’t report signs. In distinction, traditional CRISPR-Cas9 solely edited 4 p.c of cells and had minimal impact on transthyretin manufacturing.
The failure could possibly be as a result of the gene editor was confined to a small group of cells, whereas NANITE unfold to others, “enabling extra environment friendly tissue-level modifying,” wrote the workforce. Intensive liver and blood checks in mice handled with NANITE detected no poisonous negative effects.
A 3-fold enhance in modifying is only the start. The workforce is working to extend NANITE efficacy and to doubtlessly convert the system into mRNA, much like the expertise underlying Covid-19 vaccines. In comparison with shuttling round DNA into the physique—a long-standing headache—there’s a far wider vary of established supply techniques for mRNA.
Nonetheless, these early outcomes counsel it’s doable to “amplify therapeutic results by spreading cargo” past the initially edited cells. Avoiding the necessity for comparatively giant doses, NANITE might enhance the protection profile of gene-editing remedies and doubtlessly increase the expertise to tissues and organs which might be tougher to genetically alter than the liver.
The expertise modifications the numbers recreation. Even when solely a fraction of the NANITE remedy reaches its goal tissue, its skill to unfold might nonetheless ship sufficient impression to treatment at the moment untouchable genetic illnesses. “By reducing efficient dose necessities, NANITE might make genome modifying extra sensible and accessible for treating human illness,” wrote the workforce.