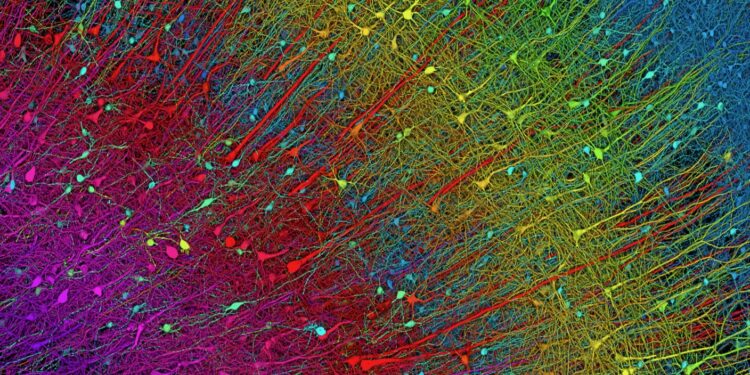
Scientists just published the most detailed map of a cubic millimeter of the human mind. Smaller than a grain of rice, the mapped part of mind consists of over 57,000 cells, 230 millimeters of blood vessels, and 150 million synapses.
The mission, a collaboration between Harvard and Google, is seeking to speed up connectomics—the examine of how neurons are wired collectively—over a a lot bigger scale.
Our brains are like a jungle.
Neuron branches crisscross areas, forming networks that course of notion, recollections, and even consciousness. Blood vessels tightly wrap round these branches to offer vitamins and vitality. Different mind cell sorts type intricate connections with neurons, assist the mind’s immune perform, and fine-tune neural community connections.
In biology, construction determines perform. Like tracing wires of a pc, mapping parts of the mind and their connections can enhance our understanding of how the mind works—and when and why it goes flawed. A mind map that charts the jungle inside our heads might assist us sort out among the most perplexing neurological issues, comparable to Alzheimer’s illness, and decipher the origins of feelings, ideas, and behaviors.
Aided by machine studying instruments from Google Analysis, the Harvard staff traced neurons, blood vessels, and different mind cells at nanoscale ranges. The pictures revealed beforehand unknown quirks within the human mind—together with mysterious tangles in neuron wiring and neurons that join by means of a number of “contacts” to different cells. General, the dataset incorporates an enormous 1.4 petabytes of knowledge—roughly the storage quantity of a thousand high-end laptops—and is free to explore.
“It’s a bit of bit humbling,” Dr. Viren Jain, a neuroscientist at Google and examine creator, instructed Nature. “How are we ever going to actually come to phrases with all this complexity?” The database, first launched as a preprint paper in 2021, has already garnered a lot enthusiasm within the scientific subject.
“It’s most likely probably the most computer-intensive work in all of neuroscience,” Dr. Michael Hawrylycz, a computational neuroscientist on the Allen Institute for Mind Science, who was not concerned within the mission, told MIT Know-how Evaluation.
Why So Sophisticated?
Many varieties of mind maps exist. Some chart gene expression in mind cells; others map totally different cell sorts throughout the mind. However the objective is identical. They goal to assist scientists understand how the brain works in health and disease.
The connectome particulars highways between mind areas that “speak” to one another. These connections, referred to as synapses, quantity within the tons of of trillions in human brains—on the size of the variety of stars within the universe.
Many years in the past, the primary whole-brain wiring map detailed all 302 neurons within the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans. As a result of its genetics are largely identified, the lowly worm delivered insights, comparable to how the mind and physique talk to extend wholesome longevity. Subsequent, scientists charted the fruit fly connectome and located the underpinnings of spatial navigation.
Extra lately, the MouseLight Project and MICrONS have been deciphering a small chunk of a mouse’s mind—the outermost space referred to as the cortex. It’s hoped such work may also help inform neuro-inspired AI algorithms with decrease energy necessities and better efficacy.
However mice usually are not folks. Within the new examine, scientists mapped a cubic millimeter of human mind tissue from the temporal cortex—a nexus that’s essential for reminiscence, feelings, and sensations. Though simply one-millionth of a human mind, the trouble reconstructed connections in 3D at nanoscale decision.
Slice It Up
Sourcing is a problem when mapping the human mind. Mind tissues quickly deteriorate after trauma or loss of life, which modifications their wiring and chemistry. Mind organoids—”mini-brains” grown in check tubes—considerably resemble the mind’s structure, however they will’t replicate the actual factor.
Right here, the staff took a tiny little bit of mind tissue from a 45-year-old lady with epilepsy throughout surgical procedure—the final resort for individuals who endure extreme seizures and don’t reply to medicine.
Utilizing a machine like a deli-meat slicer armed with a diamond knife, the Harvard staff, led by connectome skilled Dr. Jeff Lichtman, meticulously sliced the pattern into 5,019 cross sections. Every was roughly 30 nanometers thick—a fraction of the width of a human hair. They imaged the slices with an electron microscope, capturing nanoscale mobile particulars, together with the “factories” inside cells that produce vitality, remove waste, or transport molecules.
Piecing these 2D photos right into a 3D reconstruction is a complete headache. A decade in the past, scientists needed to do it by hand. Jain’s staff at Google developed an AI to automate the job. The AI was capable of monitor fragments of complete parts—say, part of a neuron (its physique or branches)—and stick them again collectively all through the photographs.
In whole, the staff pieced collectively 1000’s of neurons and over 100 million synaptic connections. Different mind parts included blood vessels and myelin—a protecting molecular “sheath” masking neurons. Like electrical insulation, when myelin deteriorates, it causes a number of mind issues.
“I keep in mind this second, going into the map and taking a look at one particular person synapse from this lady’s mind, after which zooming out into these different hundreds of thousands of pixels,” Jain told Nature. “It felt form of non secular.”
A Entire New World
Even a cursory have a look at the information led to shocking insights into the mind’s intricate neural wiring.
Cortical neurons have a forest-like construction for enter and a single “cable” that delivers output indicators. Known as axons, these are dotted with 1000’s of synapses connecting to different cells.
Often, a synapse grabs onto only one spot of a neighboring neuron. However the brand new map discovered a uncommon, unusual group that connects with as much as 50 factors. “We’ve all the time had a concept that there could be tremendous connections, if you’ll, amongst sure cells…However it’s one thing we’ve by no means had the decision to show,” Dr. Tim Mosca, who was not concerned within the work, told In style Science. These may very well be extra-potent connections that enable neural communications to enter “autopilot mode,” like when using a motorbike or navigating acquainted neighborhoods.
More odd constructions included “axon whorls” that wrapped round themselves like tangled headphones. An axon’s most important goal is to achieve out and join with different neurons—so why do some fold into themselves? Do they serve a goal, or are they only a hiccup in mind wiring? It’s a thriller. One other unusual statement discovered pairs of neurons that completely mirrored one another. What this symmetry does for the mind can also be unknown.
The underside line: Our understanding of the mind’s connections and internal workings continues to be solely scratching the floor. The brand new database is a breakthrough, however it’s not good. The outcomes are from a single individual with epilepsy, which might’t signify everybody. Some wiring modifications, for instance, could also be because of the dysfunction. The staff is planning a follow-up to separate epilepsy-related circuits from these which can be extra common in folks.
In the meantime, they’ve opened the entire database for anybody to discover. And the staff can also be working with scientists to manually look at the outcomes and remove potential AI-induced errors throughout reconstruction. Up to now, tons of of cells have been “proofread” and validated by people, however it’s only a fraction of the 50,000 neurons within the database.
The know-how may also be used for different species, such because the zebrafish—one other animal mannequin typically utilized in neuroscience analysis—and ultimately the complete mouse mind.
Though this examine solely traced a tiny nugget of the human mind, the atlas is a surprising technique to peek inside its seemingly chaotic wiring and make sense of issues. “Additional research utilizing this useful resource might convey worthwhile insights into the mysteries of the human mind,” wrote the staff.
Picture Credit score: Google Analysis and Lichtman Lab