A collaborative research performed by Duke-NUS and the NUS Mechanobiology Institute brings new hope for treating neurodevelopmental issues by reactivating dormant neural stem cells and revealing extra mechanisms concerned in mind improvement.
Researchers at Duke-NUS Medical School and the Mechanobiology Institute on the National University of Singapore have recognized a brand new pathway to activate dormant neural stem cells. This discovery may result in progressive therapies for neurodevelopmental issues, together with autism, studying disabilities, and cerebral palsy.
Within the mammalian grownup mind, most neural stem cells, which originate from the nervous system and might develop into varied varieties of mind cells, keep dormant till they obtain particular indicators that activate them. As soon as woken up, they produce new neurons, aiding in mind restore and progress.
Defects in neural stem cell activation are related to aging-related cognitive decline and neurodevelopmental issues akin to microcephaly, a situation the place a child’s head is far smaller than anticipated as a result of its mind has not developed correctly. Neurodevelopmental issues have an effect on round 5 % of youngsters and adolescents worldwide and result in impaired cognition, communication, adaptive habits, and psychomotor abilities.
Analysis Utilizing Fruit Flies
To review this activation, the scientists turned to Drosophila or fruit flies. Just like mammals, the neural stem cells of fruit flies keep dormant until they’re woke up. Their findings, revealed in Science Advances, confirmed {that a} kind of glial cell named astrocytes—historically thought to offer structural and dietary assist—are essential for waking up dormant neural stem cells within the brains of fruit flies.
Utilizing super-resolution microscopy with 10 occasions magnifying energy, the crew of scientists examined the tiny fiber buildings which might be an indicator of dormant neural stem cells of fruit flies. These tremendous buildings, round 1.5 µm in diameter (or 20 occasions smaller than the diameter of a human hair), are protrusions extending from the cell physique, and are wealthy in actin or protein filaments. A particular kind of Formin protein can activate these filaments and trigger them to assemble.
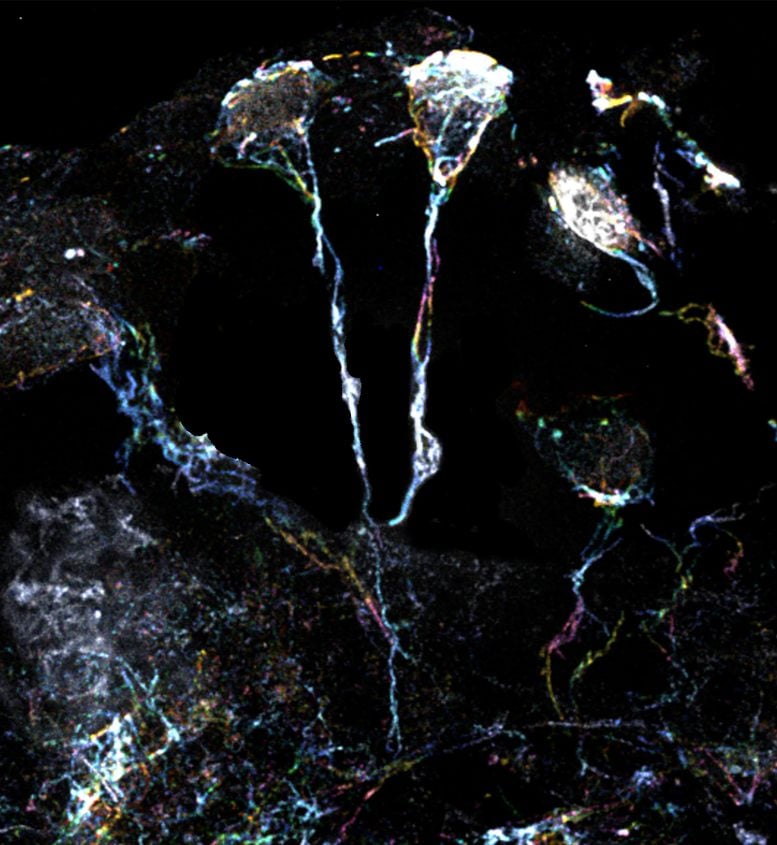
Dr. Lin Kun Yang, who was a analysis fellow at Duke-NUS on the time of the research and the primary writer, mentioned: “We determined to house in on this pathway as variants in Formin ranges are related to neurodevelopmental issues like microcephaly in people. Understanding this pathway may present new insights into creating options to deal with neurodevelopmental issues.”
The scientists noticed that astrocytes launch a kind of signaling protein known as Folded gastrulation or Fog, which sparks a sequence response that features activating the Formin protein pathway to regulate the motion of actin filaments. Finally, these processes rouse neural stem cells from their dormant state. They then begin to divide, creating new neurons that contribute to mind restore and improvement.
Significance of GPCR Proteins
The receptor protein named GPCR in neural stem cells then responds to Fog secreted from astrocytes, activating the signaling pathway that controls the formation of actin filaments in neural stem cells. GPCRs have main roles in elementary cell processes. Consequently, the GPCR protein household has grow to be a significant drug goal for therapies of assorted human illnesses: 34 % of FDA-approved medication goal this household of proteins. Subsequently, understanding how this signaling pathway controls neural stem cell reactivation could present a possible technique for utilizing current medication to deal with neurodevelopmental issues.
Professor Wang Hongyan, Appearing Programme Director of Duke-NUS’ Neuroscience & Behavioural Problems Analysis Programme; and the senior writer of the research, mentioned: “Our findings add new information to the restricted physique of analysis on mechanisms governing the reactivation of dormant neural stem cells. With our discovery of astrocytes as a key participant within the reactivation of neural stem cells, we now have a brand new method to affect neural stem cell habits.”
Professor Patrick Tan, Senior Vice-Dean for Analysis at Duke-NUS, mentioned: “This not solely advances our elementary understanding of how astrocytes affect mind cell improvement but additionally opens new avenues for advancing therapies for neurological issues, mind ageing, and harm.”
The scientists are at present investigating different indicators from astrocytes which may affect the exercise of neural stem cells. Additionally they plan to discover whether or not comparable mechanisms are concerned within the improvement of the human mind.
Duke-NUS is a pacesetter in medical analysis and schooling, with a dedication to enhancing affected person care via progressive scientific discovery. This research is a part of its ongoing efforts to deepen understanding of the basic mechanisms at play within the human mind to create new therapeutic approaches, particularly for sufferers with neurological situations.
Reference: “Astrocytes management quiescent NSC reactivation through GPCR signaling–mediated F-actin reworking” by Kun-Yang Lin, Mahekta R. Gujar, Jiaen Lin, Wei Yung Ding, Jiawen Huang, Yang Gao, Ye Sing Tan, Xiang Teng, Low Siok Lan Christine, Pakorn Kanchanawong, Yusuke Toyama and Hongyan Wang, 24 July 2024, Science Advances.
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adl4694
This work was primarily supported by the Nationwide Analysis Basis, Singapore below the Nationwide Medical Analysis Council (NMRC) Open Fund – Particular person Analysis Grant (MOH-000143) and Open Fund – Younger Particular person Analysis Grant (MOH-001236) and administered by the Singapore Ministry of Well being via the NMRC Workplace, MOH Holdings Pte Ltd, with extra assist from a number of different grants.