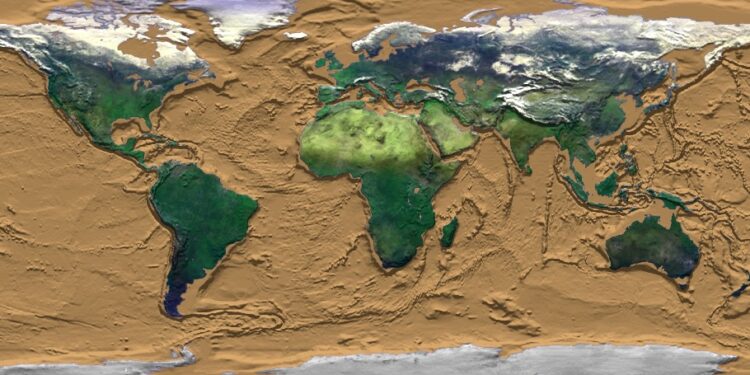
Utilizing data from contained in the rocks on Earth’s floor, my colleagues and I’ve reconstructed the plate tectonics of the planet during the last 1.8 billion years.
It’s the first time Earth’s geological report has been used like this, wanting thus far again in time. This has enabled us to make an try at mapping the planet during the last 40 p.c of its historical past, which you’ll be able to see within the animation beneath.
The work, led by Xianzhi Cao from the Ocean College in China, was recently published within the open-access journal Geoscience Frontiers.
A Stunning Dance
Mapping our planet by its lengthy historical past creates a beautiful continental dance—mesmerizing in itself and a piece of pure artwork.
It begins with the map of the world acquainted to everybody. Then India quickly strikes south, adopted by components of Southeast Asia as the past continent of Gondwana varieties within the Southern Hemisphere.
Round 200 million years in the past (Ma or mega-annum within the reconstruction), when the dinosaurs walked the earth, Gondwana linked with North America, Europe, and northern Asia to kind a big supercontinent referred to as Pangaea.
Then, the reconstruction carries on again by time. Pangaea and Gondwana had been themselves shaped from older plate collisions. As time rolls again, an earlier supercontinent referred to as Rodinia seems. It doesn’t cease right here. Rodinia, in flip, is shaped by the breakup of a good older supercontinent referred to as Nuna about 1.35 billion years in the past.
Why Map Earth’s Previous?
Among the many planets within the photo voltaic system, Earth is exclusive for having plate tectonics. Its rocky floor is cut up into fragments (plates) that grind into one another and create mountains or cut up away and kind chasms which can be then crammed with oceans.
Other than inflicting earthquakes and volcanoes, plate tectonics additionally pushes up rocks from the deep earth into the heights of mountain ranges. This fashion, parts which had been far underground can erode from the rocks and wash into rivers and oceans. From there, residing issues could make use of those parts.
Amongst these important parts is phosphorus, which varieties the framework of DNA molecules, and molybdenum, which is utilized by organisms to strip nitrogen out of the environment and make proteins and amino acids—constructing blocks of life.
Plate tectonics additionally exposes rocks that react with carbon dioxide within the environment. Rocks locking up carbon dioxide is the principle management on Earth’s local weather over very long time scales—a lot, for much longer than the tumultuous local weather change we’re accountable for at present.
A Instrument for Understanding Deep Time
Mapping the previous plate tectonics of the planet is the primary stage in having the ability to construct a whole digital model of Earth by its historical past.
Such a mannequin will enable us to check hypotheses about Earth’s previous. For instance, why Earth’s local weather has gone by excessive “Snowball Earth” fluctuations or why oxygen built up in the atmosphere when it did.
Certainly, it would enable us to significantly better perceive the suggestions between the deep planet and the floor programs of Earth that help life as we all know it.
So A lot Extra to Study
Modeling our planet’s previous is crucial if we’re to know how vitamins turned obtainable to energy evolution. The first evidence for complex cells with nuclei—like all animal and plant cells—dates to 1.65 billion years in the past.
That is close to the beginning of this reconstruction and near the time the supercontinent Nuna shaped. We goal to check whether or not the mountains that grew on the time of Nuna formation could have offered the weather to energy advanced cell evolution.
A lot of Earth’s life photosynthesizes and liberates oxygen. This hyperlinks plate tectonics with the chemistry of the environment, and a few of that oxygen dissolves into the oceans. In flip, plenty of important metals—like copper and cobalt—are extra soluble in oxygen-rich water. In sure situations, these metals are then precipitated out of the answer: Briefly, they kind ore deposits.
Many metals kind within the roots of volcanoes that happen alongside plate margins. By reconstructing the place historical plate boundaries lay by time, we are able to higher perceive the tectonic geography of the world and help mineral explorers to find historical metal-rich rocks now buried below a lot youthful mountains.
On this time of exploration of different worlds within the photo voltaic system and past, it’s value remembering there’s a lot about our personal planet we’re solely simply starting to glimpse.
There are 4.6 billion years of it to analyze, and the rocks we stroll on include the proof for a way Earth has modified over this time.
This primary try at mapping the final 1.8 billion years of Earth’s historical past is a leap ahead within the scientific grand problem to map our world. However it’s simply that—a primary try. The following years will see appreciable enchancment from the place to begin we now have now made.
The creator wish to acknowledge this analysis was largely finished by Xianzhi Cao, Sergei Pisarevsky, Nicolas Flament, Derrick Hasterok, Dietmar Muller and Sanzhong Li; as a co-author, he is only one cog within the analysis community. The creator additionally acknowledges the numerous college students and researchers from the Tectonics and Earth Methods Group at The College of Adelaide and nationwide and worldwide colleagues who did the elemental geological work this analysis relies on.
This text is republished from The Conversation below a Inventive Commons license. Learn the original article.
Picture Credit score: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio