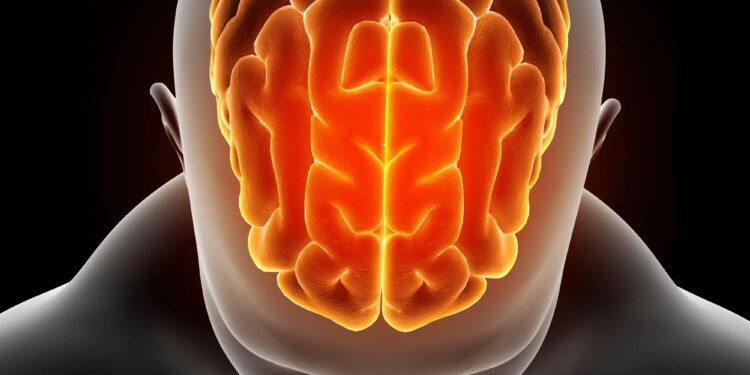
Older people with restricted social contact present a higher discount in mind quantity, particularly in areas affected by dementia, in comparison with these with frequent interactions, in response to a current examine.
People within the older age bracket with restricted social interplay could also be at the next threat of experiencing a discount in total mind quantity, notably in areas which can be usually impacted by dementia, in comparison with their counterparts who have interaction in common social interactions, in response to a examine just lately revealed in Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
Nevertheless, it is very important be aware that the examine solely found a correlation between social isolation and mind quantity lower and doesn’t show that social isolation causes mind shrinkage.
“Social isolation is a rising downside for older adults,” mentioned examine creator Toshiharu Ninomiya, MD, PhD, of Kyushu University in Fukuoka, Japan. “These outcomes counsel that offering assist for folks to assist them begin and keep their connections to others could also be useful for stopping mind atrophy and the event of dementia.”
The examine concerned 8,896 folks with a mean age of 73 who didn’t have dementia. That they had MRI mind scans and well being exams. To find out social contact, folks had been requested one query: How usually are you involved with kinfolk or mates who don’t stay with you (e.g., assembly or speaking on the cellphone)? The alternatives for answering had been daily, a number of occasions per week, a number of occasions a month, and rarely.
The folks with the bottom quantity of social contact had total mind quantity that was considerably decrease than these with probably the most social contact. The overall mind quantity, or the sum of white and gray matter, as a proportion of the whole intracranial quantity, or the amount inside the skull, together with the mind, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid, was 67.3% within the lowest contact group in comparison with 67.8% within the highest contact group. In addition they had decrease volumes in areas of the mind such because the hippocampus and amygdala that play a job in reminiscence and are affected by dementia.
The researchers took under consideration different elements that might have an effect on mind quantity, akin to age, diabetes, smoking, and train.
The socially remoted folks additionally had extra small areas of harm within the mind, known as white matter lesions, than the folks with frequent social contact. The share of intracranial quantity made up of white matter lesions was 0.30 for the socially remoted group, in comparison with 0.26 for probably the most socially related group.
The researchers discovered that signs of melancholy partly defined the connection between social isolation and mind volumes. Nevertheless, signs of melancholy accounted for under 15% to 29% of the affiliation.
“Whereas this examine is a snapshot in time and doesn’t decide that social isolation causes mind atrophy, some research have proven that exposing older folks to socially stimulating teams stopped and even reversed declines in mind quantity and improved pondering and reminiscence abilities, so it’s potential that interventions to enhance folks’s social isolation might forestall mind quantity loss and the dementia that usually follows,” Ninomiya mentioned.
Because the examine concerned solely older Japanese folks, a limitation is that the findings will not be generalizable to folks of different ethnicities and youthful folks.
Reference: “Affiliation Between Frequency of Social Contact and Mind Atrophy in Neighborhood-Dwelling Older Folks With out Dementia – The JPSC-AD Examine” by Naoki Hirabayashi, Takanori Honda, Jun Hata, Yoshihiko Furuta, Mao Shibata, Tomoyuki Ohara, Yasuko Tatewaki, Yasuyuki Taki, Shigeyuki Nakaji, Tetsuya Maeda, Kenjiro Ono, Masaru Mimura, Kenji Nakashima, Jun-ichi Iga, Minoru Takebayashi and Toshiharu Ninomiya, 12 July 2023, Neurology.
DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000207602
The examine was supported by the Japan Company for Medical Analysis and Improvement and Suntory Holdings Restricted.