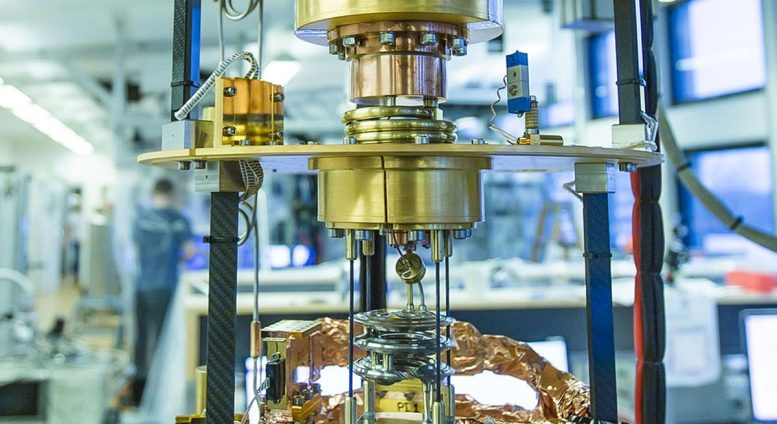

The most important problem within the growth of the quantum laptop consists of the magnetic and electrical noise that disturbs the quantum impact, and due to this fact the processor QPU (Quantum Processing Unit) is cooled all the way down to the bottom attainable temperature simply above absolutely the zero level of -273 levels. This occurs within the cryostat, which may be seen within the image. The processor is positioned on the backside of the cryostat. Credit score: Ola J. Joensen, NBI
Scientists around the globe work laborious to rinse quantum techniques for noise, which can disturb the perform of tomorrow’s highly effective quantum computer systems. Researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute (NBI) have discovered a method to make use of noise to course of quantum data. This raises the efficiency of the quantum computing unit, the qubit.
A global collaboration led by scientists on the Niels Bohr Institute (NBI), College of Copenhagen, has demonstrated another strategy. Their technique permits to make use of noise to course of quantum data. In consequence, the efficiency of the elemental quantum computing unit of data, the qubit, is elevated by 700 p.c.
The outcomes had been revealed just lately within the journal Nature Communications.
“Avoiding noise in quantum techniques has confirmed tough, since nearly any change within the surroundings can spoil issues. As an example, your system could also be working at a given magnetic or electrical subject, and if that subject modifications simply barely the quantum results disintegrate. We recommend a totally totally different strategy. As a substitute of eliminating noise, we use steady real-time noise surveillance and adapt the system as modifications within the surroundings occur,” says Ph.D. Researcher at NBI Fabrizio Berritta, lead writer on the research.
The brand new strategy is feasible because of latest developments in a number of high-tech fields.
“Beforehand, say twenty years in the past, it will have been attainable to visualise the fluctuations after the experiment, however it will have been too sluggish to make the most of this data through the precise experiment. We use FPGA (field-programmable-gate-array, ed.) expertise to get the measurements in real-time. And additional, we use machine studying to hurry up the evaluation,” explains Fabrizio Berritta, persevering with:
“The entire thought is to get the measurements and do the evaluation in the identical microprocessor that adjusts the system in real-time. Else, the scheme wouldn’t be quick sufficient for quantum computing functions.”
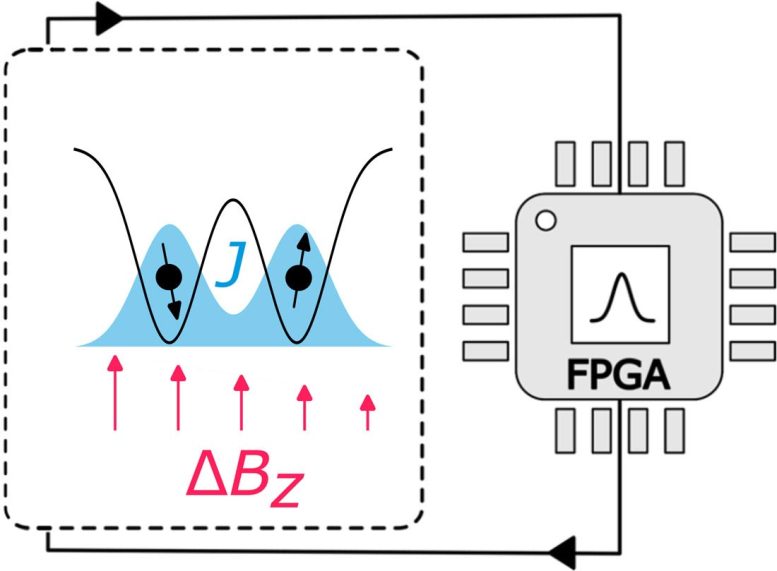
A qubit is the superior quantum computing equal to a bit. The mission’s qubit consists of two electrons trapped in a crystal. The spin of the electrons (right here one has downward spin, the opposite upward) may be managed by altering the magnetic subject gradient ΔBz. Nevertheless, each magnetic and electrical noise have an effect on this gradient. A FPGA (Discipline-Programmable Gate Array) microprocessor constantly measures the extent of noise and adjusts to modifications in real-time. Credit score: Fabrizio Berritta
Quantum Properties Add Worth
In current computing, the fundamental unit of transferable data, often known as the bit, is tied to the cost of electrons. It may possibly have solely one in all two values, one or zero – both there are electrons or there aren’t. The corresponding quantum computing unit – often known as the qubit – will be capable of assume greater than two values. The quantity of data contained per qubit will enhance exponentially with the variety of quantum properties one is ready to management, maybe leading to computer systems which are mind-blowingly extra highly effective than typical computer systems at some point.
One cornerstone of quantum mechanics is for the elementary particles to not simply have a mass and a cost but in addition a spin. One other key time period is entanglement. Right here, two or extra particles work together in such a method that the quantum state of a single particle can’t be described independently of the state of the opposite(s).
The protocol behind the brand new findings integrates a singlet-triplet spin qubit carried out in a gallium arsenide double quantum dot with FPGA-powered qubit controllers. The qubit includes two electrons, with the states of each electrons entangled.
Prof. Ferdinand Kuemmeth has been the supervisor of Fabrizio Beritta throughout his PhD mission on the Heart for Quantum Units on the Niels Bohr Institute on the College of Copenhagen. Credit score: Fabrizio Berritta
Interdisciplinary Workforce Effort
Identical to different spin qubits, the singlet-triplet qubit is susceptible to even small disturbances of their surroundings. The physicists use the time period “noise”, which shouldn’t be taken actually as acoustic noise. In relation to quantum techniques, disturbances like electrical or magnetic subject fluctuations can spoil the quantum state(s) of curiosity.
To show the helpful use of environmental fluctuations, the researchers selected this qubit as a result of its coupling to each magnetic noise and electrical noise is nicely understood from a collection of earlier research at NBI, led by Professor Ferdinand Kuemmeth, heading a analysis group on semiconducting and superconducting quantum units at NBI.
Funded by the EU, the brand new research introduced collectively analysis teams at NBI, Purdue College, Norwegian College of Science and Know-how, firms QDevil (Copenhagen), and Quantum Machines (Tel Aviv) throughout a variety of fields akin to qubit supplies, qubit fabrication, qubit management {hardware}, quantum data idea, and machine studying.
“This collaboration illustrates that the event of quantum computer systems is now not an exercise that may be pushed by particular person physics teams. Take away any one in all our companions, and this work wouldn’t have been attainable,” says Ferdinand Kuemmeth.
A Higher Strategy to Noise
The researchers see the brand new protocol as a milestone in the direction of the event of quantum computer systems, but in addition understand that many different milestones should be achieved.
“The subsequent step for us will likely be to use our protocol to techniques of various supplies and with multiple qubit,” says Fabrizio Berritta, concluding:
“I can’t say after we will see the primary really helpful quantum laptop. Perhaps ten years from now. In any case, we consider to have give you a promising strategy. Many colleagues give attention to eliminating noise to develop higher qubits, as an example by bettering the standard of the supplies used to manufacture the qubits. We’ve demonstrated that beneath sure situations one can actively modify for a few of the noise. This could possibly be related for different kinds of qubits in addition to the kind in our research.”
Reference: “Actual-time two-axis management of a spin qubit” by Fabrizio Berritta, Torbjørn Rasmussen, Jan A. Krzywda, Joost van der Heijden, Federico Fedele, Saeed Fallahi, Geoffrey C. Gardner, Michael J. Manfra, Evert van Nieuwenburg, Jeroen Danon, Anasua Chatterjee and Ferdinand Kuemmeth, 23 February 2024, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45857-0













