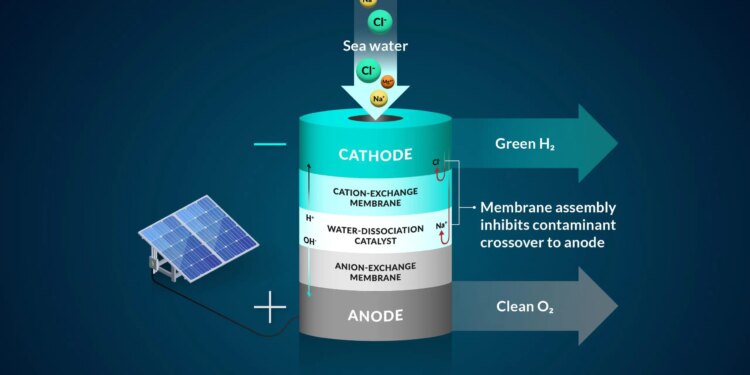
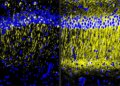
A illustration of the staff’s bipolar membrane system that converts seawater into hydrogen gasoline. Credit score: Nina Fujikawa/SLAC Nationwide Accelerator Laboratory
The cocktail of parts in seawater, together with hydrogen, oxygen, sodium, and others, is important for all times on Earth. Nevertheless, this intricate chemical make-up poses a problem when making an attempt to separate hydrogen gasoline for sustainable power purposes.
Just lately, a staff of scientists from the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford University, University of Oregon, and Manchester Metropolitan College has found a technique to extract hydrogen from the ocean. They accomplish this by funneling seawater by means of a double-membrane system and electrical energy.
Their modern design proved profitable in producing hydrogen gasoline with out producing massive quantities of dangerous byproducts. The outcomes of their research, lately printed within the journal Joule, may assist advance efforts to provide low-carbon fuels.
“Many water-to-hydrogen programs at the moment attempt to use a monolayer or single-layer membrane. Our research introduced two layers collectively,” stated Adam Nielander, an affiliate workers scientist with the SUNCAT Middle for Interface Science and Catalysis, a SLAC-Stanford joint institute. “These membrane architectures allowed us to regulate the best way ions in seawater moved in our experiment.”
Hydrogen gasoline is a low-carbon gasoline presently utilized in some ways, reminiscent of to run fuel-cell electrical automobiles and as a long-duration power storage possibility – one that’s suited to retailer power for weeks, months, or longer – for electrical grids.
Many makes an attempt to make hydrogen gasoline begin with recent or desalinated water, however these strategies may be costly and power intensive. Handled water is less complicated to work with as a result of it has much less stuff – chemical parts or molecules – floating round. Nevertheless, purifying water is dear, requires power, and provides complexity to units, the researchers stated. An alternative choice, pure freshwater, additionally accommodates quite a few impurities which can be problematic for contemporary expertise, along with being a extra restricted useful resource on the planet, they stated.
To work with seawater, the staff applied a bipolar, or two-layer, membrane system and examined it utilizing electrolysis, a technique that makes use of electrical energy to drive ions, or charged parts, to run a desired response. They began their design by controlling essentially the most dangerous component to the seawater system – chloride, stated Joseph Perryman, a SLAC and Stanford postdoctoral researcher.
“There are lots of reactive species in seawater that can interfere with the water-to-hydrogen reaction, and the sodium chloride that makes seawater salty is one of the main culprits,” Perryman said. “In particular, chloride that gets to the anode and oxidizes will reduce the lifetime of an electrolysis system and can actually become unsafe due to the toxic nature of the oxidation products that include molecular chlorine and bleach.”
The bipolar membrane in the experiment allows access to the conditions needed to make hydrogen gas and mitigates chloride from getting to the reaction center.
“We are essentially doubling up on ways to stop this chloride reaction,” Perryman said.
A home for hydrogen
The ideal membrane system would perform three primary functions: separate hydrogen and oxygen gases from seawater; help move only the useful hydrogen and hydroxide ions while restricting other seawater ions; and help prevent undesired reactions. Capturing all three of these together is hard, and the team’s research is targeted toward exploring systems that can efficiently combine all three of these needs.
Specifically in their experiment, protons, which were the positive hydrogen ions, pass through one of the membrane layers to a place where they can be collected and turned into hydrogen gas by interacting with a negatively charged electrode. The second membrane in the system allows only negative ions, such as chloride, to travel through.
As an additional backstop, one membrane layer contains negatively charged groups that are fixed to the membrane, which makes it harder for other negatively charged ions, like chloride, to move to places where they shouldn’t be, said Daniela Marin, a Stanford graduate student in chemical engineering and co-author. The negatively-charged membrane proved to be highly efficient in blocking almost all of the chloride ions in the team’s experiments, and their system operated without generating toxic byproducts like bleach and chlorine.
Along with designing a seawater-to-hydrogen membrane system, the study also provides a better general understanding of how seawater ions move through membranes, the researchers said. This knowledge can help scientists design stronger membranes for other applications as well, such as producing oxygen gas.
“There is also some interest in using electrolysis to produce oxygen,” Marin said. “Understanding ion flow and conversion in our bipolar membrane system is critical for this effort, too. Along with producing hydrogen in our experiment, we also showed how to use the bipolar membrane to generate oxygen gas.”
Next, the team plans to improve their electrodes and membranes by building them with materials that are more abundant and easily mined. This design improvement could make the electrolysis system easier to scale to a size needed to generate hydrogen for energy-intensive activities, like the transportation sector, the team said.
The researchers also hope to take their electrolysis cells to SLAC’s Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL), where they can study the atomic structure of catalysts and membranes using the facility’s intense X-rays.
“The future is bright for green hydrogen technologies,” said Thomas Jaramillo, professor at SLAC and Stanford and director of SUNCAT. “The fundamental insights we are gaining are key to informing future innovations for improved performance, durability, and scalability of this technology.”
Reference: “Hydrogen production with seawater-resilient bipolar membrane electrolyzers” by Daniela H. Marin, Joseph T. Perryman, McKenzie A. Hubert, Grace A. Lindquist, Lihaokun Chen, Ashton M. Aleman, Gaurav A. Kamat, Valerie A. Niemann, Michaela Burke Stevens, Yagya N. Regmi, Shannon W. Boettcher, Adam C. Nielander and Thomas F. Jaramillo, 11 April 2023, Joule.
DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2023.03.005
This project is supported by the U.S. Office of Naval Research; the Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability Accelerator; the DOE’s Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Chemical Sciences, Geosciences, and Biosciences Division through the SUNCAT Center for Interface Science and Catalysis, a SLAC-Stanford joint institute; and the DOE’s Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Fuel Cell Technologies Office.